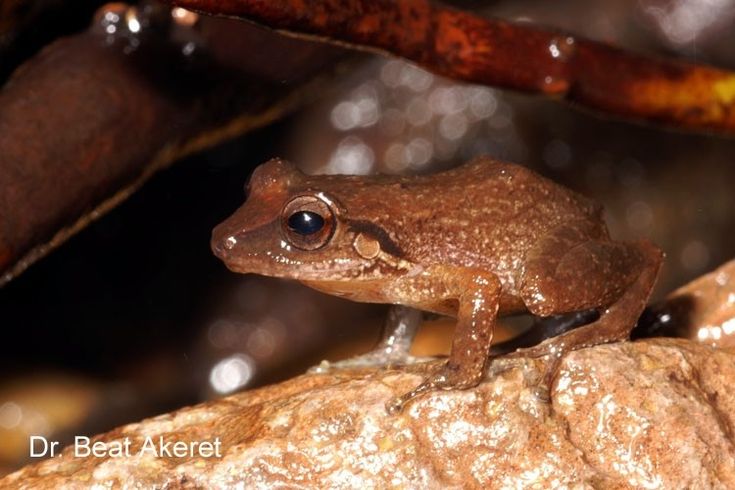

The Barlagne Frog
Context
Amphibians, such as the Barlagne Frog, play a crucial role in their ecosystems by regulating insect populations and serving as prey for many predators. In Guadeloupe, these amphibians are particularly vulnerable to environmental disturbances. Protecting their natural habitats is essential to ensure their survival and the preservation of the island’s biodiversity.
Description
The Barlagne Frog, scientifically named Eleutherodactylus barlagnei, is a small amphibian endemic to Guadeloupe, belonging to the family Eleutherodactylidae. It is a relatively discreet frog, recognizable by its modest size and coloration, which allows it to blend effectively into its forest habitat.
- Size : Approximately 2 to 3 cm in length.
- Coloration : The coloration is generally brownish or gray with patterns that slightly vary between individuals, helping it remain less visible in forest environments.
- Morphology : It has smooth skin and short limbs, adapted to a primarily terrestrial and sometimes semi-aquatic lifestyle.
Habitat
The Barlagne Frog is primarily found in the humid tropical forests of Guadeloupe, particularly in mountainous areas and the dense forests of Basse-Terre.
- Habitat Type : Humid tropical forests, especially shaded areas near streams and zones of high moisture.
- Altitude : Prefers higher elevations where humidity is high and temperatures are moderate.
Lifestyle
The Barlagne Frog is a nocturnal amphibian with specific behaviors and adaptations:
- Behavior : It is generally active at night, hiding under leaf litter, rocks, or dense vegetation during the day.
- Diet : Its diet is primarily insectivorous, feeding on small arthropods found in its forest habitat.
- Reproduction : Reproduction occurs in moist environments. Females lay their eggs in damp areas where they develop directly into young frogs without an aquatic larval stage. Eggs are typically deposited on the soil surface or in slightly humid locations.
Importance and threat
The Barlagne Frog plays an important role in its ecosystem:
- Ecological Role: It helps control insect populations and participates in the food chain as an insect predator.
- Indicator of Ecological Health: Its presence and health status can serve as indicators for assessing the quality of forest habitats and soil moisture.
The Barlagne Frog is threatened by several factors, mainly due to human activities and environmental changes:
- Habitat Loss : Deforestation and the destruction of its natural habitat for agriculture and urban development are major threats.
- Climate Change : Variations in temperature and humidity caused by climate change can affect the availability of its habitat and living conditions.
- Pollution : Water and soil pollution can also impact habitat quality and the health of this species.
Sources
- Fiches d’Identification des Amphibiens de Guadeloupe : Parc national de la Guadeloupe (guadeloupe-parcnational.fr)
- Guide des Amphibiens des Antilles
- Articles sur la Biodiversité de la Guadeloupe
- IUCN Red List : Informations sur les espèces menacées et leurs habitats.
- Herpetological Conservation and Biology : Recherche sur les amphibiens des Caraïbes.
- Wildlife Conservation International : Informations sur la conservation des espèces endémiques des Antilles.
Informations
-
-
Scientific name
Eleutherodactylus barlagnei
-
Location
